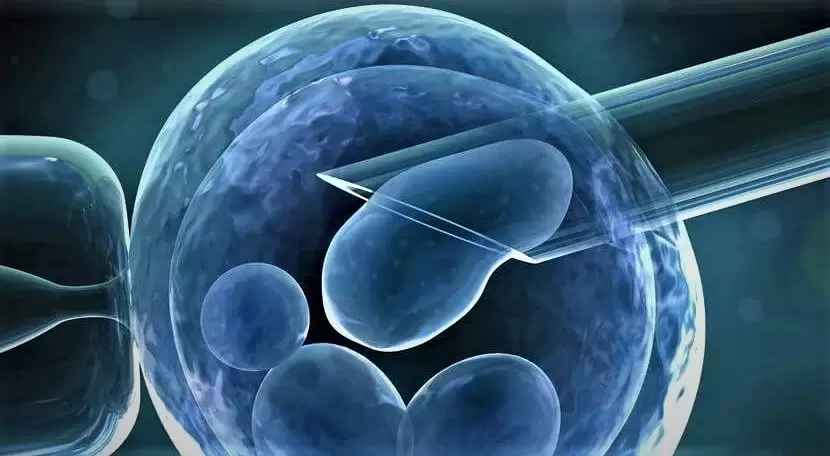
Preimplantation genetic screening (PGS) is a type of genetic screening test based on the determination of the correct number of chromosomes of the cells in an embryo. Chromosomal abnormalities are responsible for the failure of the implantation of the embryo into the uterine cavity and of miscarriage.
Although PGS is not a test for a specific genetic disorder, the Down syndrome – also known as trisomy 21 which is characterized by the presence of an extra chromosome 21 – can be detected by PGS.
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) is another genetic screening test used to detect the presence of mutated genes for specific genetic disorders or diseases, such as Huntigton disease, Marfan syndrome, Cystic fibrosis, Tay-Sachs disease, X chromosome related genetic diseases (Hemophilia, Duchene muscular dystrophy), abnormalities in the number of chromosomes.
This test is crucial to prevent passing genetic disease or disorders on to a child, if there is a family history in one or both of the couples.
What is Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD)?
Thanks to the developments in genetics, it is possible to conduct advanced examinations on embryos developed through in vitro fertilization treatment. The examinations carried out for this purpose are generally called preimplantation genetic diagnosis or embryo genetic diagnosis.
Embryo genetic screening tests are performed by taking 1 or more cells from embryos that develop as a result of fertilization of egg and sperm cells in a laboratory environment. Thanks to the use of certain special methods on the cells taken, numerical and structural chromosome disorders of the babies that may develop with the development of the embryos and single gene diseases such as sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis and Thalassemia can be diagnosed.
Among the factors that cause in vitro fertilization attempts to fail, the first is that the embryos are genetically unhealthy. Unhealthy embryos have a low chance of attaching to the uterus. If they attach to the uterus, the risk of miscarriage is higher. Therefore, PGD, known as the embryo genetic screening test, is applied to examine whether the embryos are genetically healthy before they are transferred to the uterus. Healthy embryos are selected and transferred to the mother’s uterus. With this procedure, it is possible to increase the success rate of IVF treatment.
There is a risk that hereditary diseases carried by the mother and father will be transferred to the children. Therefore, it should not be forgotten that determining genetic diseases in couples and embryos is extremely important in terms of having healthy children. Thanks to the PGD procedure performed using different techniques, it is possible to detect many hereditary diseases at the embryo level.
PGD can be applied to couples at risk of single-gene diseases or structural chromosomal disorders/translocations. The PGD technique can also be used in the gender selection process to prevent certain diseases transmitted depending on the X chromosome. Cystic fibrosis, spinal muscular atrophy, thalassemia and sickle cell anemia are the single-gene diseases that most often cause PGD. In cases of recurrent miscarriage, advanced maternal age or unsuccessful IVF attempts, the PGD procedure may be considered.
PGD can increase the success of IVF and pregnancy rates in suitable cases. It can reduce the risk of miscarriage and the need for medical termination of pregnancy. PGD helps reduce the rate of multiple pregnancies and also reduces the economic and psychological burdens resulting from repeated unsuccessful IVF attempts.
What is Preimplantation Genetic Screening (PGS)?
PGS techniques, which stand out as a holistic screening method, can be used to determine whether the embryo has a normal number of chromosomes. With the PGS technique, embryos are evaluated for chromosomal anomalies before being placed in the uterus. The chance of having a healthy baby can be increased by detecting and transferring embryos with no anomalies.
The most common chromosomal anomaly is having fewer or more chromosomal anomalies than normal. This condition, also called aneuploidy, can be present in the egg or sperm or occur in the embryo during the fertilization stage.
With the PGS procedure, genetic screening is performed on embryos and the genetic structure of the embryos is evaluated. With this procedure, it is possible to determine whether there is a structural or numerical problem in the chromosomes. In order to perform this procedure, a sample must be taken from the embryo with a laser under a microscope. Usually, blastomere and morphoectoderm biopsy taken from the embryo is used.
After the classical in vitro fertilization treatment stimulation, the collected eggs are combined with sperm by microinjection method on the same day and the obtained embryos are followed until the blastocyst stage. Biopsy is performed on the trophoectoderm layer of embryos with suitable quality for biopsy, cell samples are taken and the embryos are frozen one by one. If embryos with normal chromosome sequence are detected after genetic analysis, frozen embryo transfer process is planned.
PGS stands out as a modern approach that basically allows screening of embryos in terms of all chromosomes without causing any damage and detecting healthy embryos. With the transfer of a single embryo that is determined to have a chromosomal normal structure, the pregnancy rate of patients from all age groups can be increased and the risk of losing the pregnancy to miscarriage can be reduced.
Working Hours
- Monday: 09:00 – 18:00
- Tuesday: 09:00 – 18:00
- Wednesday: 09:00 – 18:00
- Thursday: 09:00 – 18:00
- Friday: 09:00 – 18:00
- Saturday: 09:00 – 18:00
- Sunday: Closed
