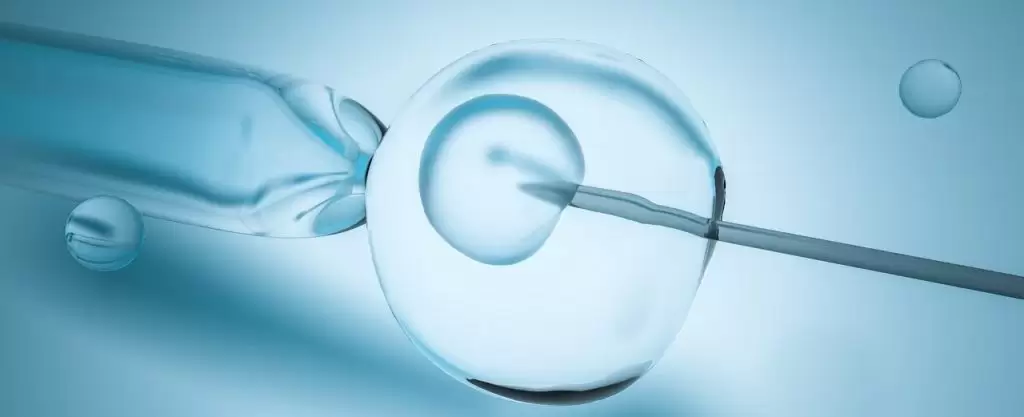

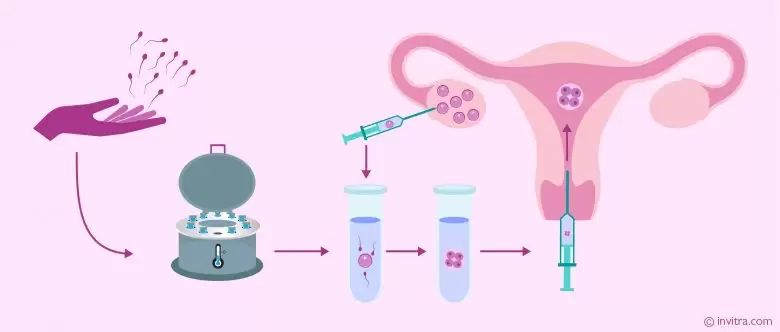
Embryo transfer is a simple procedure characterized by transferring of the in vitro fertilized embryo into the uterine cavity by means of a catheter loaded with embryo during the IVF.
The transfer is carried out at 2-8 cell stage of the embryogenesis.
The embryo can be transferred at any time (1-6 days after retrieved the egg), but usually between 2-4 days.
During in vitro fertilization treatment, the process of placing embryos obtained outside the mother’s body in a laboratory environment is called embryo transfer. Egg cells collected from the mother are fertilized in a laboratory environment with sperm cells taken from the father. Then, they are placed in the mother’s uterus. Embryo transfer can be used to help achieve pregnancy in couples who cannot have a baby naturally.
What is Embryo Transfer?
Embryo transfer is the process of leaving the embryo obtained through in vitro fertilization treatment in the uterus with the help of a thin catheter. The procedure is performed with ultrasound guidance in order to advance the catheter correctly in the uterus and place it in the most appropriate place. Although in vitro fertilization embryo transfer can sometimes be performed under anesthesia in cases such as vaginismus, it is usually a procedure that does not require anesthesia.
How is Embryo Transfer Performed?
In embryo transfer, which is the last step of in vitro fertilization treatment, the fertilized egg is placed in the uterus of the expectant mother after it becomes an embryo in the laboratory. The embryo taken into the catheter is placed in the uterus after the catheter is passed through the vaginal opening and the cervix.
In in vitro fertilization treatment, embryo transfer is performed on average 4 to 6 days after the egg collection procedure. In this context, fresh embryos, frozen embryos, 3-day and 5-day embryos can be transferred. A single embryo or multiple embryos can be transferred during the procedure.
Today, the transfer of a single embryo that is 5 days old and has reached the blastocyst stage is generally preferred. Couples who wish can freeze the embryos not used in IVF treatment for later use.
The stage and number of embryo transfers are determined for each couple. Fresh embryos are embryos obtained during treatment, and fresh embryo transfers are performed in most IVF treatments.
In general, 10 to 15 egg cells are obtained in top baby treatment. Only one of the many embryos obtained after fertilization is transferred. The obtained quality embryos can be frozen according to the couple’s wishes and used in the next case of need. Especially in couples whose first IVF treatment was unsuccessful, using frozen embryos instead of starting the treatment over again can help shorten the process.
Embryos can also vary depending on the day they are transferred. Cell division has occurred in embryos transferred on the third day after fertilization, but growth has not started. Embryos enter the blastocyst stage on the fifth day after fertilization. There are 60 to 120 cells in a blastocyst, which is larger than a three-day embryo. Pregnancy is more likely to occur as a result of blastocyst transfer.
Since some embryos lose their vitality before reaching the blastocyst stage, it is generally believed that embryos that reach the blastocyst stage are genetically healthier and more normal. It is also possible to choose a quality embryo from among the blastocyst stage embryos. In order for genetic diagnosis and tests to be performed before implantation, the embryo must have reached the blastocyst stage.
When is Embryo Transfer Performed?
Embryo transfer is performed between days 2 and 6 after the egg collection process after evaluating different criteria such as the development of the embryo, its number, the patient’s age, and the number of previous attempts.
Before the healthy embryo is transferred to the mother’s uterus, a genetic examination can be performed before the transfer to check if there is an anomaly in the chromosomes. In this context, a few cells are taken from healthy embryos and examined in a laboratory environment. Embryo transfer is performed according to the results obtained after the examination.
In some cases, a genetic diagnosis is required before the transfer. During the genetic examination, a possible genetic disease or chromosomal disorder is investigated. If the in vitro fertilization treatment in the couple has failed more than once, if the previous pregnancy ended in miscarriage, if at least one of the couples or their families has a genetic disorder or chromosomal disorder, a genetic examination should be performed before the embryo transfer.
Genetic examination can be performed with two different methods depending on the day it is performed. In the FISH method, a single cell taken on the third day of the embryos is stained with a dye and examined under a microscope.
It is known that the ACGh and NGS methods developed in recent years provide much more consistent and detailed results than the FISH method. In this method, which has been increasingly preferred especially since 2013, approximately 7-8 cells are taken when the embryo is approximately on its fifth day. Thus, all 24 chromosomes can be examined separately, provided that the X and Y chromosomes are examined.
With genetic examination before embryo transfer, it is possible to detect chromosomal disorders or single gene diseases in the mother or father. After the examination, a healthy embryo is selected and embryos that may cause possible diseases are eliminated.
In recent years, genetic examination has been preferred in advanced age pregnancies, even if there is no chromosomal or genetic disorder. In women, the quality of the egg begins to decrease significantly after the age of 40. This may also mean that there is deformation in the eggs. The healthiest embryos can be selected with genetic examination performed before embryo transfer.
What are the Symptoms After Embryo Transfer?
The symptoms of attachment after embryo transfer are among the most curious topics for couples. Most women who become pregnant with IVF treatment do not experience any symptoms. However, couples expect some symptoms to occur during the period between the embryo transfer and the pregnancy test. Although many people may think that the treatment has failed if there are no pregnancy symptoms after the embryo transfer, this is not true.
In IVF treatment, it is determined whether the transferred embryo will adhere or not after an average of 9 to 11 days. At the end of this period, the result can be learned by performing a pregnancy test in blood.
If the blood test performed 9 to 11 days after the embryo is placed gives a positive result, it can be understood that the first stage of IVF treatment has been successfully completed. Although some symptoms may be experienced after the embryo transfer, these are not proof that the pregnancy process has started.
Expectant mothers may experience various symptoms before learning the test results after IVF treatment. Symptoms after embryo transfer include abdominal pain, cramps, nausea, lower back and back pain.
Some women may not experience these symptoms in the early stages. This should not cause fear or anxiety. Even if these symptoms are not experienced, it is possible for the embryo to settle in the uterus and the pregnancy period to begin.
In the following process, the pregnancy symptoms of natural pregnancy and IVF pregnancies are similar. Early IVF retention symptoms that usually occur after the embryo settles in the uterus in IVF treatment are as follows:
Pelvic discomfort and mild cramping
Nausea
Tension and tenderness in the breasts
Psychological and mental fluctuations
Morning sickness
Things to Consider After Embryo Transfer
The most important point after embryo transfer is the correct use of medications. Attention should be paid to the way the medications are used, the hours of application and the doses. Strenuous physical activities such as running can affect the rate of pregnancy due to both vibration effects and the increase in body temperature. Therefore, strenuous physical activities should be avoided.
Sugar and processed foods should not be consumed after embryo transfer, protein and oily fish should be included in the diet program. Folic acid and necessary multivitamins should also be used. Raw meat, milk and fresh cheese should be avoided due to the risk of possible infection.
Working Hours
- Monday: 09:00 – 18:00
- Tuesday: 09:00 – 18:00
- Wednesday: 09:00 – 18:00
- Thursday: 09:00 – 18:00
- Friday: 09:00 – 18:00
- Saturday: 09:00 – 18:00
- Sunday: Closed
